low flow low gradient aortic stenosis ase
Echocardiography is the key tool for the diagnosis and evaluation of aortic stenosis. 40 ms a mean gradient 40 mm Hg or an aortic valve area.
This discordant echocardiographic data creates doubts about the severity of the disease.

. Low flow low gradient aortic stenosis with reduced LVEF. LFLGAS occurs in 30 to 50 of patients with severe AS5 It shows an AVA low gradient. True-severe classical and paradoxical low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis can be distinguished from pseudo-severe aortic stenosis.
Low flow low gradient aortic stenosis with preserved LVEF. In this case the mean Gradient is 40 mm Hg so is clear it is a severe aortic stenosis. Highlights in this focused update on aortic stenosis document include.
It is indeed a low gradient AS still you are not convinced since the 2D look of the valve looks severe. So the Low Flow Low gradient severe Ao Stenosis is existing. AVA.
Low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis is a difficult entity to diagnose and treat. AHA ACC Guidelines. Low flow low gradient aortic stenosis.
Various diagnostic modalities are needed to accurately determine the severity of aortic stenosis and potential treatment benefit. Indicator Mild Moderate Severe. Faeez Mohamad Ali Vindhya Wilson Rajesh NairPublish Year.
Then you find the culprit. But dont forget the PEDOFF. An important proportion of patients with aortic stenosis AS have a low-gradient AS ie.
Low-LVEF Classical Low-Flow Low-Gradient LVEF25 SV42mL MG25mmHg. An important proportion of patients with aortic stenosis AS have a low-gradient AS ie. A low flow state is defined as a cardiac index 30 lminm2 or a stroke volume of 35mlm2.
Jet velocity 30 ms 30 40 40 ms Mean gradient 25 mmHg 25 40 40 mmHg Valve area 15 cm210 15 10 cm2. Aortic stenosis patients with severe LV dysfunction and low cardiac output present with relatively low transvalvular gradients. By transesophageal echocardiography a significant number of patients with severe aortic stenosis are reclassified particularly in the low flow and low flow low gradient severe aortic stenosis groups.
TABLE 1 Outcome and Impact of Aortic Valve Replacement in Patients With Aortic Stenosis According to the FlowGradient Category First Author Year Ref. Aortic valve replacement AVR if the patient has symptoms or. A LF-LG severe aortic stenosis is defined as an aortic valve AVA 10 cm2 or indexed 06 cm2m2 a mean transvalvular gradient 40 mmHg and a LVEF 40.
True-severe classical and paradoxical low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis can be distinguished from pseudo-severe aortic stenosis by dobutamine stress. Aortic stenosis AS is defined as a peak aortic jet velocity. The former condition is severe AS with LV dysfunction and latter is pr.
This entity is defined as an LVEF 50 the presence of a low flow stroke volume index Author. Adda J Mielot C Giorgi R et al. In Normal or High flow Conditions SV 35 mLm2 Low Flow Low EF Severe AS.
This is called LG-ASone type What is paradoxical -Low flow-Low. Eur Heart J 2016. Theless severe AS can be present in patients with low forward flow resulting in a peak valve velocity aortic valve gra-dient low-flowlow-gradient AS LFLGAS.
In both cases the decrease in gradient relative to AS severity is due to a reduction in transvalvular flow. The course will discuss some anatomical. Paradoxical low-flow aortic valve stenosis is defined as the presence of small valve area cw severe Aortic stenosis low transvalvular gradients non -severe range in the presence of low transvalvular flow but with normal ejection fraction 50.
Background Recent studies and current clinical observations suggest that some patients with severe aortic stenosis on the basis of aortic valve area may paradoxically have a relatively low gradient despite the presence of a preserved left ventricular LV ejection fraction. AS grading algorithm- an integrated and stepwise approach. Various diagnostic modalities are needed to accurately determine the severity of aortic stenosis and potential treatment benefit.
The objective of the present study was to document the prevalence potential mechanisms and. New classification of AS by gradient flow and ejection fraction. Clavel MA Magne J Pibarot P.
Low-flow low-gradient LF-LG aortic stenosis AS may occur with depressed or preserved left ventricular ejection fraction LVEF and both situations are among the most challenging encountered in patients with valvular heart disease. Its a complicated entity and the treatment is still debated even if some patients would probably take advantage of the aortic valve replacement. Low-flow low-gradient severe aortic stenosis despite normal ejection fraction is associated with severe left ventricular dysfunction as assessed by speckle-tracking echocardiography.
The management of this subset of patients is particularly challenging because the AVA-gradient discrepancy raises uncertainty about the. Because of the lowflow state the transvalvular peak velocity and pressure gradient may underestimate the stenosis severity whereas the aortic valve area AVA may overestimate the severity. Left ventricular LV systolic dysfunction defined as LV ejec-.
Of Patients Mean Age yrs Endpoint MortalityEvent Rates and BenefitofAVR Moderate AS Low-Gradient AS High-Gradient AS Group With The Highest Mortality NFLG LFLG NFHG LFHG Event Rate. About 30 of patients with AS and preserved LVEF 50 have a low-flow state. A small aortic valve area AVA.
Because clinical decision-making is based on the echocardiographic assessment of its severity it is essential that standards be adopted to maintain accuracy and consistency across echocardiographic laboratories. 24 25 Paradoxical LFLGAS is defined by an AVA. Low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis is a difficult entity to diagnose and treat.
Lowflow lowgradient LFLG aortic stenosis AS is one of the most challenging cardiovascular conditions in terms of diagnosis and therapeutic management. It is difficult to distinguish them from aortic sclerosis and LV dysfunction with low cardiac output. A small aortic valve area AVA.
We diagnose a case of significant aortic stenosis but desperately miss to pick an adequate gradient across the valve. It is the dysfunctional ventricle pulling down the gradient.

Aortic Stenosis Low Flow Low Gradient What S The Hype
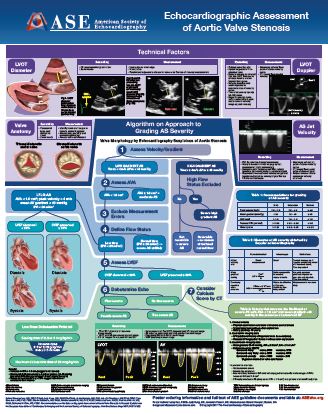
Aortic Valve Stenosis Poster American Society Of Echocardiography

Confirmation Of Aortic Stenosis Severity In Case Of Discordance Between Aortic Valve Area And Gradient Sciencedirect

Prognosis Of Severe Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis By Stroke Volume Index And Transvalvular Flow Rate Jacc Cardiovascular Imaging

Echocardiographic Assessment Of Aortic Valve Stenosis A Focused Update

Resolving Apparent Inconsistencies Between Area Flow And Gradient Measurements In Patients With Aortic Valve Stenosis And Preserved Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction American Journal Of Cardiology

Evaluation Of Patients With Low Flow Low Gradient Severe Aortic Download Scientific Diagram

Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis When Is It Severe American College Of Cardiology

Integration Of Flow Gradient Patterns Into Clinical Decision Making For Patients With Suspected Severe Aortic Stenosis And Preserved Lvef A Systematic Review Of Evidence And Meta Analysis Sciencedirect

Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis When Is It Severe American College Of Cardiology

Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis When Is It Severe American College Of Cardiology

Complex Scenarios Low Gradient In Low Ef As Patients
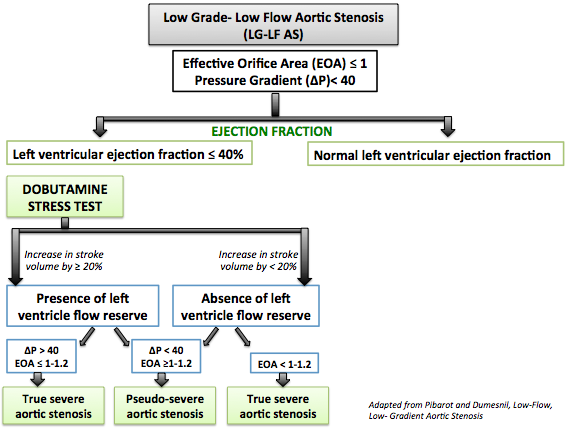
Aortic Stenosis Echocardiography Wikidoc

Aortic Stenosis Low Flow Low Gradient What S The Hype
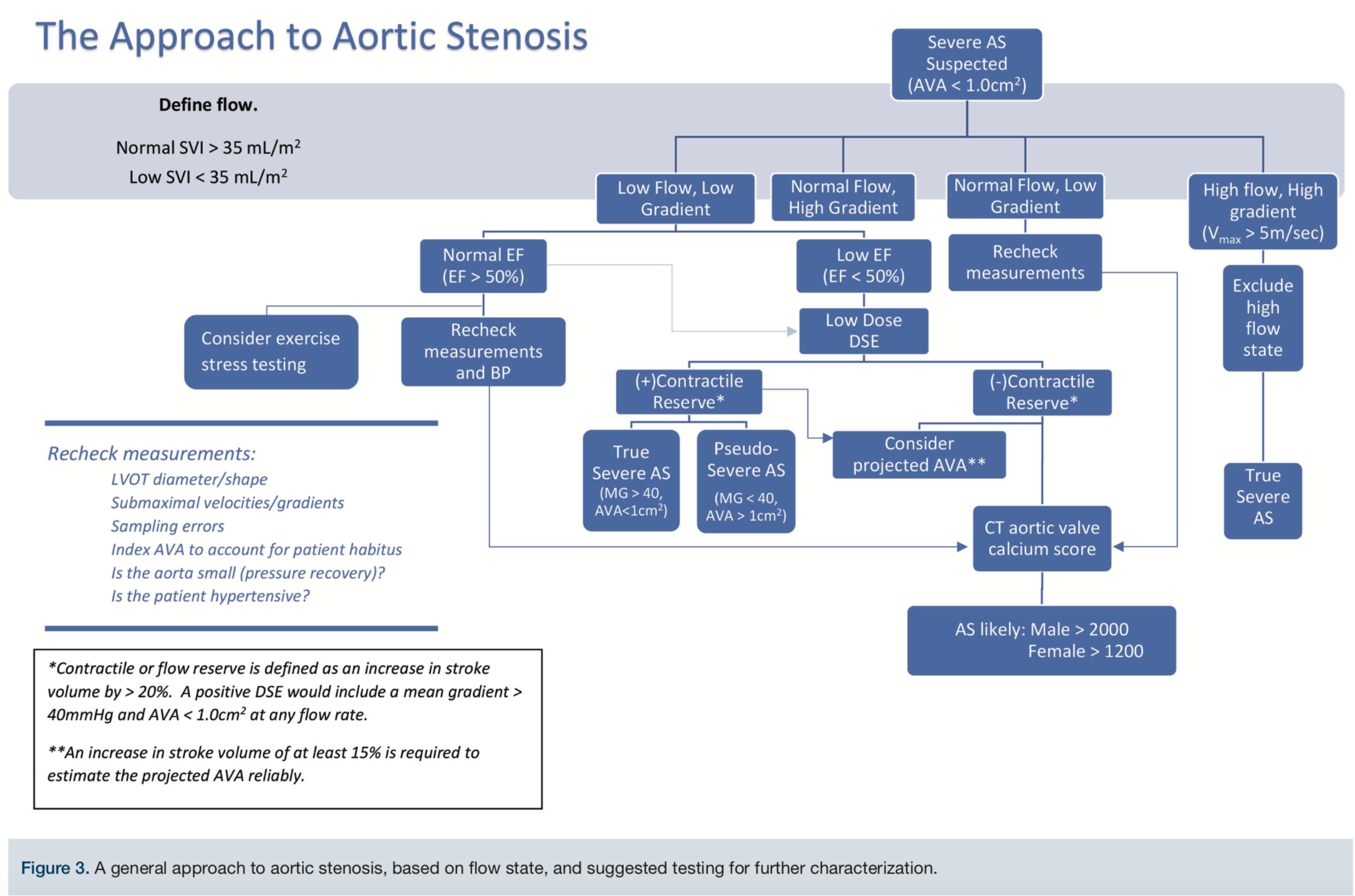
What Type Of As Does Your Patient Have Sorting Out Differences In The Low Flow Low Gradient Severe As Patients

Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Still A Diagnostic And Therapeutic Challenge Vogelgesang 2017 Clinical Cardiology Wiley Online Library

Paradoxical Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Effect Of Low Transvalvular Flow Conditions On Indexed Stroke Volume After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement Journal Of The American Society Of Echocardiography

What Type Of As Does Your Patient Have Sorting Out Differences In The Low Flow Low Gradient Severe As Patients